How-To-Test-Electrical-and-Electronics-Components-with-Multimeter.jpg' alt='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Files' title='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Files' />Manufacture of data acquisition, power meters, power quality analyzer PQA, LCR meters, battery measurement, multi meters and field measuring instruments. In addition to the sensor characteristics, you must consider the required hardware and software to properly condition, acquire, and visualize microphone measurements. Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf EditorView and Download Hanna Instruments HI 991301 instruction manual online. Waterproof pHECTDSTemperature Meters with Advanced Features. HI 991301 Multimeter pdf. Pages in category Measuring instruments The following 200 pages are in this category, out of approximately 415 total. This list may not reflect recent changes. How to Measure Amps electrical service, circuit or individual device electrical current usage rate AMPS MEASUREMENT METHODS How to measure amperage or amps. Measuring Sound with Microphones National Instruments. What Is sound pressure Pressure variations, whether in the air, the water, or another medium the human ear can detect, are considered sounds. The human eardrum transfers pressure oscillations, or sound, into electrical signals that our brains interpret as music, speech, noise, and so on. Microphones are designed to do the same thing. You can then record and analyze these signals to gather information about the nature of the path the sound took from the source to the microphone. For example, in noise, vibration, and harshness test, engineers are usually interested in reducing undesirable sounds, such as the noise passengers in a car experience while driving. This could include sounds that are above or below the frequencies the human ear can detect or amplitudes at specific resonant frequencies. These measurements are important to designers who need to reduce noise to meet emissions standards or to characterize a device for performance and longevity. Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Converter' title='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Converter' />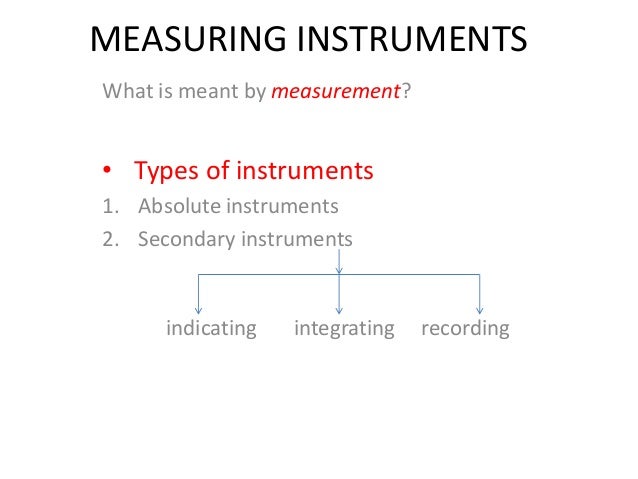 Sound pressure is the most common measurement performed because humans are exposed to sound and can detect sound pressure. Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg'>Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg. Measured in pascals Pa, the sound pressure level represents how a receiver perceives sound. You can also determine the sound power of a source. Measured in watts W, the sound power level represents the total acoustic energy that is radiated in all directions. It is independent of the environment including the room, receivers, or distance from the source. Power is a property of the source, whereas sound pressure depends on the environment, reflecting surfaces, the distance of the receiver, ambient sounds, and so on. Back to Top. 2. How do microphones work You can choose from a few different designs for microphones, but the most common instrumentation microphones are externally polarized condenser microphones, prepolarized electret condenser microphones, and piezoelectric microphones. Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' title='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' />Figure 1. A microphone is a transducer that converts acoustical waves into electrical signals. Condenser Microphones. A condenser microphone operates on a capacitive design. It incorporates a stretched metal diaphragm that forms one plate of a capacitor. A metal disk placed close to the diaphragm acts as a backplate. When a sound field excites the diaphragm, the capacitance between the two plates varies according to the variation in the sound pressure. A stable DC voltage is applied to the plates through a high resistance to keep electrical charges on the plate. The change in the capacitance generates an AC output proportional to the sound pressure. The charge of this capacitor is generated either by an external polarizing voltage or by the properties of the material itself, as in the case of prepolarized microphones. Externally polarized microphones need 2. V from an external power supply. Prepolarized microphones are powered by IEPE preamplifiers that require a constant current source. Figure 2. The most common instrumentation microphone, a condenser microphone, operates on a capacitive design. Piezoelectric Microphones. Piezoelectric microphones use a crystal structure to generate the backplate voltage. Many piezoelectric microphones use the same signal conditioning as accelerometers and may use IEPE signal conditioning to provide the polarization voltage. Although these sensor type microphones have low sensitivity levels, they are durable and able to measure high amplitude pressure ranges. Conversely, the floor noise level on this type of microphone is generally high. This design is suitable for shock and blast pressure measurement applications. Back to Top. 3. How do I choose the right microphone Response Field. You must choose the microphone that is best for the type of field in which you will operate it. The three types of measurement microphone are free field, pressure field, and random incidence. These microphones operate similarly at lower frequencies but differently at higher frequencies. A free field microphone measures the sound pressure from a single source directly at the microphone diaphragm. It measures sound pressure as it existed before the microphone was introduced into the sound field. These microphones work best in open areas free of hard or reflective surfaces. Anechoic chambers or larger open areas are ideal for free field microphones. Figure 3. Free Field Microphone. A pressure field microphone is designed to measure the sound pressure in front of the diaphragm. It has the same magnitude and phase at any position in the field. It is usually found in an enclosure, or cavity, which is small when compared with wavelength. Pressure field microphone application examples include testing the pressure exerted on walls, on airplane wings, or inside structures such as tubes, housings, or cavities. Figure 4. Pressure Field Microphone. In many situations, the sound is not traveling from a single source. Random incidence or diffuse field microphones respond uniformly to sounds arriving simultaneously from all angles. You use this type of microphone when taking sound measurements in a church or an area with hard, reflective walls. However, for most microphones, the pressure and random incidence responses are similar, so pressure field microphones are often used for random incidence measurements. Figure 5. Random Incidence Microphone. Dynamic Range. The main criterion for describing sound is based on the amplitude of the sound pressure fluctuations. Otome Games. The lowest amplitude that a healthy human ear can detect is 2. Pa. Since the pressure numbers represented by pascals are generally low and not easily managed, another, more commonly used scale, the decibel d. B scale, was developed. This logarithmic scale more closely matches the response reactions of the human ear to the pressure fluctuations. Manufacturers specify the maximum decibel level based on the design and physical characteristics of the microphone. The specified maximum d. B level refers to the point where the diaphragm approaches the backplate, or where total harmonic distortion THD reaches a specified amount, typically 3 percent THD. The maximum decibel level that a microphone outputs in a certain application depends on the voltage supplied and that particular microphones sensitivity. Before you can calculate the maximum output for a microphone using a specific preamplifier and its corresponding peak voltage, you first need to calculate the pressure in pascals that the microphone can accept. You can calculate the amount of pressure using the following formula Where P pascals Pa and voltage is the preamplifier output peak voltage. After determining the maximum pressure level that the microphone can sense at its peak voltage, you can convert this amount to decibels d. B using the following logarithmic scale Where P pressure in pascals. Po reference pascals constant 0. PaThis formula provides the maximum rating that a microphone, when combined with a specific preamplifier, is capable of measuring. For the low end noise level, or minimum amount of pressure required, you need to review the cartridge thermal noise CTN rating of the microphone. The CTN specification provides the lowest measurable sound pressure level that can be detected above the electrical noise inherent within the microphone. Figure 6 shows the typical representation of the noise level at different frequencies for a microphone when used in conjunction with a preamplifier.
Sound pressure is the most common measurement performed because humans are exposed to sound and can detect sound pressure. Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg'>Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg. Measured in pascals Pa, the sound pressure level represents how a receiver perceives sound. You can also determine the sound power of a source. Measured in watts W, the sound power level represents the total acoustic energy that is radiated in all directions. It is independent of the environment including the room, receivers, or distance from the source. Power is a property of the source, whereas sound pressure depends on the environment, reflecting surfaces, the distance of the receiver, ambient sounds, and so on. Back to Top. 2. How do microphones work You can choose from a few different designs for microphones, but the most common instrumentation microphones are externally polarized condenser microphones, prepolarized electret condenser microphones, and piezoelectric microphones. Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' title='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' />Figure 1. A microphone is a transducer that converts acoustical waves into electrical signals. Condenser Microphones. A condenser microphone operates on a capacitive design. It incorporates a stretched metal diaphragm that forms one plate of a capacitor. A metal disk placed close to the diaphragm acts as a backplate. When a sound field excites the diaphragm, the capacitance between the two plates varies according to the variation in the sound pressure. A stable DC voltage is applied to the plates through a high resistance to keep electrical charges on the plate. The change in the capacitance generates an AC output proportional to the sound pressure. The charge of this capacitor is generated either by an external polarizing voltage or by the properties of the material itself, as in the case of prepolarized microphones. Externally polarized microphones need 2. V from an external power supply. Prepolarized microphones are powered by IEPE preamplifiers that require a constant current source. Figure 2. The most common instrumentation microphone, a condenser microphone, operates on a capacitive design. Piezoelectric Microphones. Piezoelectric microphones use a crystal structure to generate the backplate voltage. Many piezoelectric microphones use the same signal conditioning as accelerometers and may use IEPE signal conditioning to provide the polarization voltage. Although these sensor type microphones have low sensitivity levels, they are durable and able to measure high amplitude pressure ranges. Conversely, the floor noise level on this type of microphone is generally high. This design is suitable for shock and blast pressure measurement applications. Back to Top. 3. How do I choose the right microphone Response Field. You must choose the microphone that is best for the type of field in which you will operate it. The three types of measurement microphone are free field, pressure field, and random incidence. These microphones operate similarly at lower frequencies but differently at higher frequencies. A free field microphone measures the sound pressure from a single source directly at the microphone diaphragm. It measures sound pressure as it existed before the microphone was introduced into the sound field. These microphones work best in open areas free of hard or reflective surfaces. Anechoic chambers or larger open areas are ideal for free field microphones. Figure 3. Free Field Microphone. A pressure field microphone is designed to measure the sound pressure in front of the diaphragm. It has the same magnitude and phase at any position in the field. It is usually found in an enclosure, or cavity, which is small when compared with wavelength. Pressure field microphone application examples include testing the pressure exerted on walls, on airplane wings, or inside structures such as tubes, housings, or cavities. Figure 4. Pressure Field Microphone. In many situations, the sound is not traveling from a single source. Random incidence or diffuse field microphones respond uniformly to sounds arriving simultaneously from all angles. You use this type of microphone when taking sound measurements in a church or an area with hard, reflective walls. However, for most microphones, the pressure and random incidence responses are similar, so pressure field microphones are often used for random incidence measurements. Figure 5. Random Incidence Microphone. Dynamic Range. The main criterion for describing sound is based on the amplitude of the sound pressure fluctuations. Otome Games. The lowest amplitude that a healthy human ear can detect is 2. Pa. Since the pressure numbers represented by pascals are generally low and not easily managed, another, more commonly used scale, the decibel d. B scale, was developed. This logarithmic scale more closely matches the response reactions of the human ear to the pressure fluctuations. Manufacturers specify the maximum decibel level based on the design and physical characteristics of the microphone. The specified maximum d. B level refers to the point where the diaphragm approaches the backplate, or where total harmonic distortion THD reaches a specified amount, typically 3 percent THD. The maximum decibel level that a microphone outputs in a certain application depends on the voltage supplied and that particular microphones sensitivity. Before you can calculate the maximum output for a microphone using a specific preamplifier and its corresponding peak voltage, you first need to calculate the pressure in pascals that the microphone can accept. You can calculate the amount of pressure using the following formula Where P pascals Pa and voltage is the preamplifier output peak voltage. After determining the maximum pressure level that the microphone can sense at its peak voltage, you can convert this amount to decibels d. B using the following logarithmic scale Where P pressure in pascals. Po reference pascals constant 0. PaThis formula provides the maximum rating that a microphone, when combined with a specific preamplifier, is capable of measuring. For the low end noise level, or minimum amount of pressure required, you need to review the cartridge thermal noise CTN rating of the microphone. The CTN specification provides the lowest measurable sound pressure level that can be detected above the electrical noise inherent within the microphone. Figure 6 shows the typical representation of the noise level at different frequencies for a microphone when used in conjunction with a preamplifier.
 Sound pressure is the most common measurement performed because humans are exposed to sound and can detect sound pressure. Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg'>Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg. Measured in pascals Pa, the sound pressure level represents how a receiver perceives sound. You can also determine the sound power of a source. Measured in watts W, the sound power level represents the total acoustic energy that is radiated in all directions. It is independent of the environment including the room, receivers, or distance from the source. Power is a property of the source, whereas sound pressure depends on the environment, reflecting surfaces, the distance of the receiver, ambient sounds, and so on. Back to Top. 2. How do microphones work You can choose from a few different designs for microphones, but the most common instrumentation microphones are externally polarized condenser microphones, prepolarized electret condenser microphones, and piezoelectric microphones. Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' title='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' />Figure 1. A microphone is a transducer that converts acoustical waves into electrical signals. Condenser Microphones. A condenser microphone operates on a capacitive design. It incorporates a stretched metal diaphragm that forms one plate of a capacitor. A metal disk placed close to the diaphragm acts as a backplate. When a sound field excites the diaphragm, the capacitance between the two plates varies according to the variation in the sound pressure. A stable DC voltage is applied to the plates through a high resistance to keep electrical charges on the plate. The change in the capacitance generates an AC output proportional to the sound pressure. The charge of this capacitor is generated either by an external polarizing voltage or by the properties of the material itself, as in the case of prepolarized microphones. Externally polarized microphones need 2. V from an external power supply. Prepolarized microphones are powered by IEPE preamplifiers that require a constant current source. Figure 2. The most common instrumentation microphone, a condenser microphone, operates on a capacitive design. Piezoelectric Microphones. Piezoelectric microphones use a crystal structure to generate the backplate voltage. Many piezoelectric microphones use the same signal conditioning as accelerometers and may use IEPE signal conditioning to provide the polarization voltage. Although these sensor type microphones have low sensitivity levels, they are durable and able to measure high amplitude pressure ranges. Conversely, the floor noise level on this type of microphone is generally high. This design is suitable for shock and blast pressure measurement applications. Back to Top. 3. How do I choose the right microphone Response Field. You must choose the microphone that is best for the type of field in which you will operate it. The three types of measurement microphone are free field, pressure field, and random incidence. These microphones operate similarly at lower frequencies but differently at higher frequencies. A free field microphone measures the sound pressure from a single source directly at the microphone diaphragm. It measures sound pressure as it existed before the microphone was introduced into the sound field. These microphones work best in open areas free of hard or reflective surfaces. Anechoic chambers or larger open areas are ideal for free field microphones. Figure 3. Free Field Microphone. A pressure field microphone is designed to measure the sound pressure in front of the diaphragm. It has the same magnitude and phase at any position in the field. It is usually found in an enclosure, or cavity, which is small when compared with wavelength. Pressure field microphone application examples include testing the pressure exerted on walls, on airplane wings, or inside structures such as tubes, housings, or cavities. Figure 4. Pressure Field Microphone. In many situations, the sound is not traveling from a single source. Random incidence or diffuse field microphones respond uniformly to sounds arriving simultaneously from all angles. You use this type of microphone when taking sound measurements in a church or an area with hard, reflective walls. However, for most microphones, the pressure and random incidence responses are similar, so pressure field microphones are often used for random incidence measurements. Figure 5. Random Incidence Microphone. Dynamic Range. The main criterion for describing sound is based on the amplitude of the sound pressure fluctuations.
Sound pressure is the most common measurement performed because humans are exposed to sound and can detect sound pressure. Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg'>Snow Leopard 10.6 8 Dmg. Measured in pascals Pa, the sound pressure level represents how a receiver perceives sound. You can also determine the sound power of a source. Measured in watts W, the sound power level represents the total acoustic energy that is radiated in all directions. It is independent of the environment including the room, receivers, or distance from the source. Power is a property of the source, whereas sound pressure depends on the environment, reflecting surfaces, the distance of the receiver, ambient sounds, and so on. Back to Top. 2. How do microphones work You can choose from a few different designs for microphones, but the most common instrumentation microphones are externally polarized condenser microphones, prepolarized electret condenser microphones, and piezoelectric microphones. Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' title='Electrical Measurements Measuring Instruments Pdf Download' />Figure 1. A microphone is a transducer that converts acoustical waves into electrical signals. Condenser Microphones. A condenser microphone operates on a capacitive design. It incorporates a stretched metal diaphragm that forms one plate of a capacitor. A metal disk placed close to the diaphragm acts as a backplate. When a sound field excites the diaphragm, the capacitance between the two plates varies according to the variation in the sound pressure. A stable DC voltage is applied to the plates through a high resistance to keep electrical charges on the plate. The change in the capacitance generates an AC output proportional to the sound pressure. The charge of this capacitor is generated either by an external polarizing voltage or by the properties of the material itself, as in the case of prepolarized microphones. Externally polarized microphones need 2. V from an external power supply. Prepolarized microphones are powered by IEPE preamplifiers that require a constant current source. Figure 2. The most common instrumentation microphone, a condenser microphone, operates on a capacitive design. Piezoelectric Microphones. Piezoelectric microphones use a crystal structure to generate the backplate voltage. Many piezoelectric microphones use the same signal conditioning as accelerometers and may use IEPE signal conditioning to provide the polarization voltage. Although these sensor type microphones have low sensitivity levels, they are durable and able to measure high amplitude pressure ranges. Conversely, the floor noise level on this type of microphone is generally high. This design is suitable for shock and blast pressure measurement applications. Back to Top. 3. How do I choose the right microphone Response Field. You must choose the microphone that is best for the type of field in which you will operate it. The three types of measurement microphone are free field, pressure field, and random incidence. These microphones operate similarly at lower frequencies but differently at higher frequencies. A free field microphone measures the sound pressure from a single source directly at the microphone diaphragm. It measures sound pressure as it existed before the microphone was introduced into the sound field. These microphones work best in open areas free of hard or reflective surfaces. Anechoic chambers or larger open areas are ideal for free field microphones. Figure 3. Free Field Microphone. A pressure field microphone is designed to measure the sound pressure in front of the diaphragm. It has the same magnitude and phase at any position in the field. It is usually found in an enclosure, or cavity, which is small when compared with wavelength. Pressure field microphone application examples include testing the pressure exerted on walls, on airplane wings, or inside structures such as tubes, housings, or cavities. Figure 4. Pressure Field Microphone. In many situations, the sound is not traveling from a single source. Random incidence or diffuse field microphones respond uniformly to sounds arriving simultaneously from all angles. You use this type of microphone when taking sound measurements in a church or an area with hard, reflective walls. However, for most microphones, the pressure and random incidence responses are similar, so pressure field microphones are often used for random incidence measurements. Figure 5. Random Incidence Microphone. Dynamic Range. The main criterion for describing sound is based on the amplitude of the sound pressure fluctuations.